도슐랭스타
C++ - 객체와 멤버 생성자 소멸자 this 본문
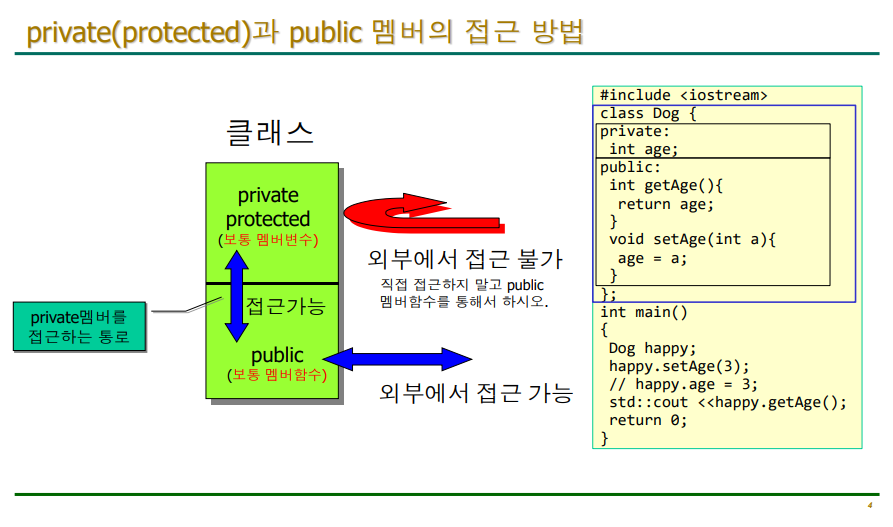

C나 C++에서 일반 객체가 멤버에 접근할 때 "."을 사용하고 포인터 객체가 멤버에 접근할 때는 "->"을 사용한다.
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge();
void setAge(int a);
};
int Dog::getAge()
{
return age;
}
void Dog::setAge(int a)
{
age = a;
}
int main()
{
Dog happy; // Dog class의 happy객체 정의
happy.setAge(3);
cout << happy.getAge() << std::endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge();
void setAge(int a);
void cry();
};
int Dog::getAge()
{
return age;
}
void Dog::setAge(int a)
{
age = a;
}
void Dog::cry() {
cout << "멍멍" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
Dog happy; // Dog class의 happy객체 정의
happy.setAge(3);
cout << happy.getAge() << std::endl;
happy.cry();
happy.cry();
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
class Dog {
private:
int age;
double weight;
std::string name;
public:
int getAge() {
return age;
}
void setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
void setWeight(double w) {
weight = w;
}
std::string getName() {
return name;
}
void setName(std::string n) {
name = n;
}
};
int main()
{
Dog happy;
happy.setAge(3);
happy.setWeight(3.5);
happy.setName("해피");
std::cout << happy.getName() << "는 "
<< happy.getAge() << "살, "
<< happy.getWeight() << "kg입니다.\n";
return 0;
}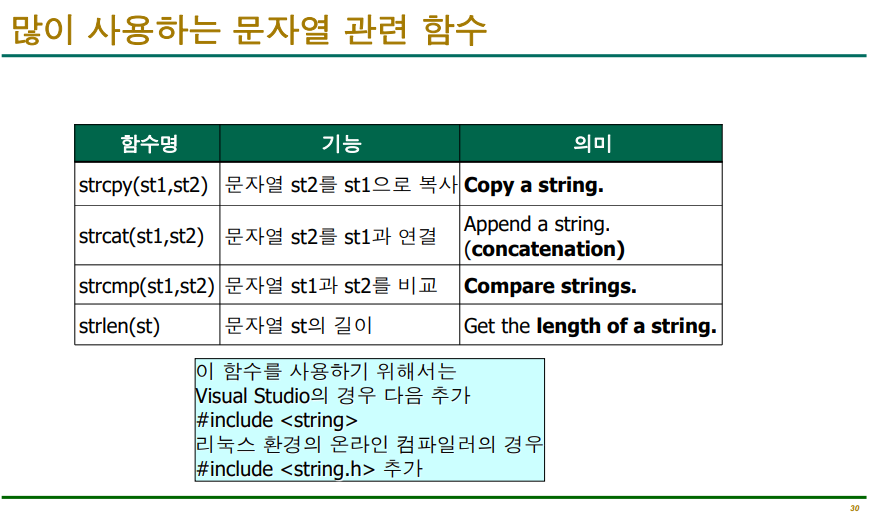
★strcpy
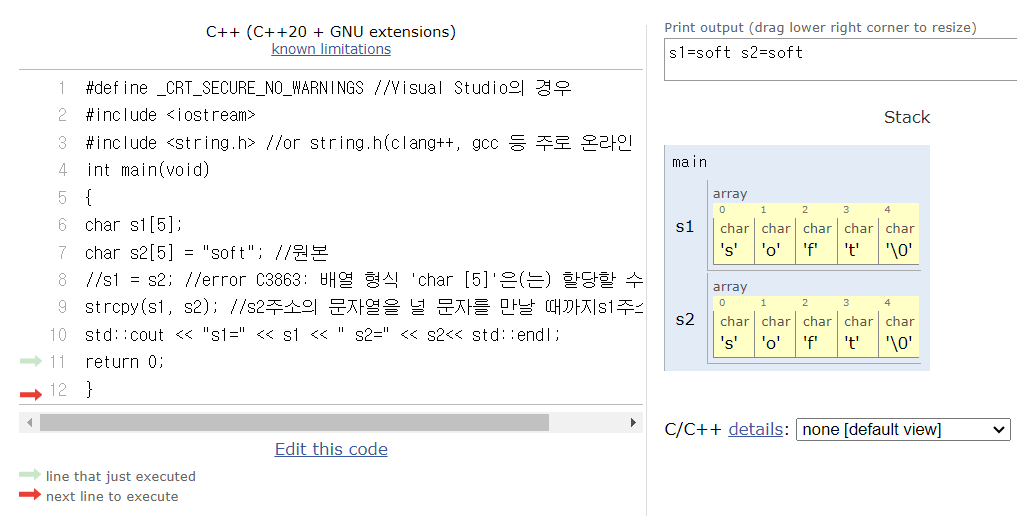
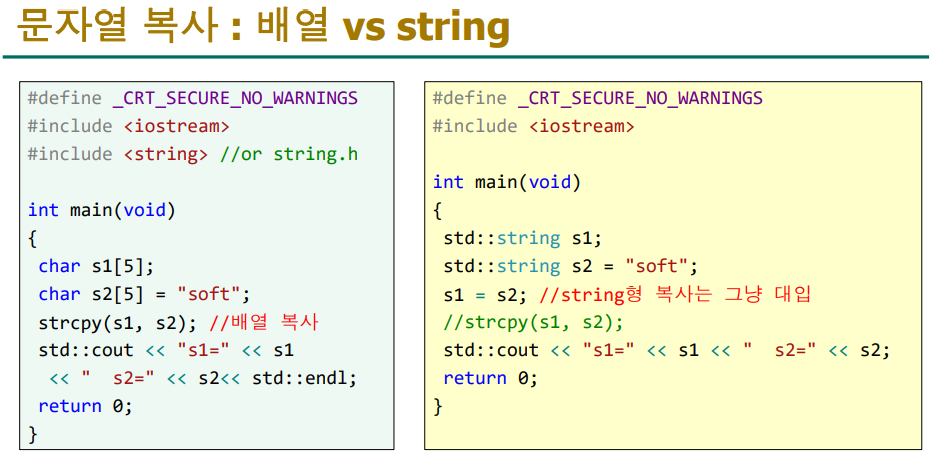
배열을 복사할 때는 'strcpy()'를 사용하고 문자열을 복사할 때는 '대입'을 하면 된다.
class의 배열 멤버
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //string.h
using std::cout;
class Cat {
private: //생략가능
int age;
char name[20]; // A
//const char *name; //B, 비추
public:
int getAge();
const char* getName();
void setAge(int a);
void setName(const char* pName);
};
int Cat::getAge()
{
return age;
}
void Cat::setAge(int a)
{
age = a;
}
void Cat::setName(const char* pName)
{
strcpy(name, pName); //A, 복사
//name=pName; //B, 주소 대입
}
const char* Cat::getName()
{
return name;
}
int main()
{
Cat nabi;
nabi.setName("나비");
nabi.setAge(3); //입력
cout << nabi.getName() << " 나이는"<<nabi.getAge()<<"살이다.";
return 0;
}class의 pivate 멤버를 배열로 했을 때 ' const char* ' 로 받으면 되고 복사는 'strcpy()'를 사용한다.
class의 string 멤버
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //string.h
using std::cout;
class Cat {
private: //생략가능
int age;
std::string name;
public:
int getAge();
std::string getName();
void setAge(int a);
void setName(std::string pName);
};
int Cat::getAge()
{
return age;
}
void Cat::setAge(int a)
{
age = a;
}
void Cat::setName(std::string pName)
{
pName = name; //복사
}
std::string Cat::getName()
{
return name;
}
int main()
{
Cat nabi;
nabi.setName("나비");
nabi.setAge(3); //입력
cout << nabi.getName() << " 나이는"<<nabi.getAge()<<"살이다.";
return 0;
}string의 복사는 '대입'을 하면 된다.
★포인터 객체
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int a) { age = a; }
};
int main()
{
Dog happy, * pd; //일반 객체 happy와 포인터 객체 pd, int x, *px;
pd = &happy; //px=&x;
happy.setAge(5); //일반 객체는 '.'으로 멤버를 접근
cout << pd->getAge(); //포인터 객체는 '->'로 멤버를 접근
return 0;
}포인터 객체는 '->'로 멤버 접근을 해야한다.

★생성자 함수는 객체가 생성될 때마다 자동을 호출된다.
생성자 함수의 리턴형을 지정하지 않아도 된다.
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
Dog() { age = 1; } // 생성자 정의, Dog():age(1){ }, Dog():age{1}{ }
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int a) { age = a; }
};
int main()
{
Dog happy, happy1; //happy객체가 생성되는 순간 생성자가 자동 호출됨
cout << happy.getAge() << std::endl;
cout << happy1.getAge() << std::endl;
return 0;
}- Dog() { age = 1;}
- Dog() : age(1) {};
- Dog() : age{1} {};
★전부 생성자 정의를 하는 방법이다.
★C++ 변수 초기화 방법
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int x=1; //copy initialization,비추
int y(2);//direct initialization
int z{3};//Uniform initialization, C++11
int z1{};//Uniform initialization, 자동으로 0,C++11
std::cout << x << y << z << z1;
}생성자의 매개변수로 멤버변수 초기화
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
Dog(int a) { age = a; } // 생성자 정의, Dog():age(1){ }, Dog():age{1}{ }
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int a) { age = a; }
};
int main()
{
Dog happy(1), h(5); //happy객체가 생성되는 순간 생성자가 자동 호출됨
cout << happy.getAge()<<h.getAge();
return 0;
}소멸자
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
Dog(int a) { age = a; } // 생성자 정의, Dog():age(1){ }, Dog():age{1}{ }
~Dog(){cout<<"소멸\n";}
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int a) { age = a; }
};
int main()
{
Dog happy(1), h(5); //happy객체가 생성되는 순간 생성자가 자동 호출됨
cout << happy.getAge()<<h.getAge();
return 0;
}★this 포인터
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
Dog(int age) { this->age = age; } // 생성자 정의, Dog():age(1){ }, Dog():age{1}{ }
~Dog(){cout<<"소멸\n";}
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int age) {
this->age = age; //private 멤버에 접근할 때는 'this->'를 사용한다.
}
};
int main()
{
Dog happy(1), h(5); //happy객체가 생성되는 순간 생성자가 자동 호출됨
cout << happy.getAge()<<h.getAge();
return 0;
}반응형
'C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C++ - 함수중첩(Function Overloading) (0) | 2023.11.15 |
|---|---|
| C++ - const new (0) | 2023.11.08 |
| C++-구조체와 클래스 (0) | 2023.10.18 |
| C++ 맛보기와 C복습(4)-구조체, 객체지향 프로그래밍 (0) | 2023.10.11 |
| C++ 맛보기와 C 복습(3)-함수, 구조체 (0) | 2023.09.27 |
Comments





